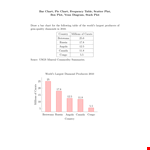
Frequency is a critical component in various aspects of data analysis, providing valuable insights and enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions.
One important aspect is notes frequency, which refers to the occurrence and distribution of notes within a dataset. By analyzing the frequency of specific notes, businesses can identify patterns, trends, or anomalies that may impact their overall operations.
Chart frequency is another key element, focusing on the frequency with which specific chart types are utilized. Understanding the popularity and effectiveness of different chart types helps organizations choose the most suitable visual representation for their data, enhancing comprehension and making it easier to communicate insights.
Total frequency encompasses a broader perspective, considering the overall frequency or occurrence of an event or variable within a given dataset. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the prevalence of certain factors, helping businesses identify dominant trends or outliers that require attention.
Location frequency delves into the analysis of geographic data, examining the frequency of events or variables across different locations. By understanding the distribution patterns, businesses can uncover regional trends, make targeted marketing efforts, or optimize their operations based on location-specific insights.
Following frequency refers to the frequency with which certain actions or behaviors are observed. Whether tracking social media interactions or website engagement metrics, analyzing following frequency provides valuable information about user behavior, enabling businesses to tailor their strategies accordingly.
Pareto chart frequency focuses on utilizing the Pareto principle, also known as the 80/20 rule, to identify and prioritize the most significant factors contributing to a specific outcome. By analyzing the frequency of specific variables, businesses can identify the vital few elements that have the most substantial impact on their operations.